December 12, 2025 | Robert Campbell
16 min read
 When the History of Search Engine Optimization is updated to include the post-Covid era, this chapter will be titled The Rise of Entity SEO with the sub header, The Shift from Strings to Things. But in truth, the shift towards ‘things’ began in 2012 with Google’s introduction of the Knowledge Graph. This update was followed by many algorithm improvements which focused on identifying and promoting the highest quality pages. In 2018, Google introduced E.E.A.T (Expertise, Experience, Authority and Trust,) which are the most stringent quality filters yet because they examine the authors’ credentials and experience. The new rules are now ruthlessly being applied in every sector, but especially to health and finance websites which are still more thoroughly monitored in order to protect web users from fraud.
When the History of Search Engine Optimization is updated to include the post-Covid era, this chapter will be titled The Rise of Entity SEO with the sub header, The Shift from Strings to Things. But in truth, the shift towards ‘things’ began in 2012 with Google’s introduction of the Knowledge Graph. This update was followed by many algorithm improvements which focused on identifying and promoting the highest quality pages. In 2018, Google introduced E.E.A.T (Expertise, Experience, Authority and Trust,) which are the most stringent quality filters yet because they examine the authors’ credentials and experience. The new rules are now ruthlessly being applied in every sector, but especially to health and finance websites which are still more thoroughly monitored in order to protect web users from fraud.
The origins of Entity SEO are buried in the A of Google EEAT. The authority of the Subject Matter Expert (SME) or the solutions provider is at the root of the push for organizational clarity that spawned Entity SEO. Our team at KPDI believes that AI-driven Search has only acted as a catalyst to help shift the industry’s approach away from strings and towards things because of an algorithmic need to define connections and quantify experience, and thus recognize, validate and grade real world Authority.
Koray Tuğberk GÜBÜR helped define Semantic SEO
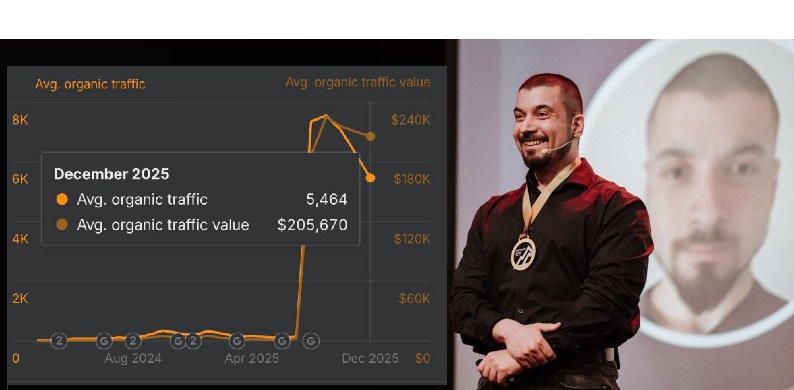
Koray Tuğberk GÜBÜR stands behind a case study wherein he used his groundbreaking Semantic SEO approach to improve and streamline page elements in order to rank higher in a competitive search landscape.
Led by Rob Campbell, the Search Experience Director, the SEO team at KPDI has been following Koray Tugberk GUBUR, reading and absorbing his Rules of Semantic SEO. A true pioneer, Koray’s Semantic SEO isn’t just about matching keywords; it’s about building deep, interconnected networks of meaning (a single comprehensive knowledge graph) around a topic to establish Topical Authority. It’s about making a web page which comprehensively details all major aspects of a particular subject, providing users with a superior answer. It’s about moving beyond simply matching and repeating keywords in FAQs and web copy, towards a more holistic presentation. It involves creating Topical Maps, understanding semantic connections, and structuring content to help search engines grasp its meaning by putting things in context, essentially mirroring how Google’s Knowledge Graph functions. Semantic SEO relies on Topical Authority Frameworks, and Koray would probably dislike the term Entity SEO, as he already complains about folks inventing new terminology to avoid using the name he coined, which is Semantic SEO.
Koray’s most notable paper, the Importance of “Entity-orientated Search” Understanding for SEO: Beyond Strings will likely be heralded as the premier pioneering doctrine outlining what we now call Entity SEO, in the months and years to come.
If you ask ChatGPT, ‘Did AI cause the shift toward Entity SEO?’ the answer engine will reply with an enthusiastic yes, but that isn’t entirely true. Koray’s paper is dated Sept 2021 which is well before the debut of ChatGPT in 2023.

“The Evolution from Strings to Things”.
Rather than relying on words, Google now understands meaning through entities and how they relate to one another. The products, people and physical infrastructure associated with something (for which you have just made a webpage) have important ‘relations’ which should be referenced in your web copy to make topical connections within a Knowledge Graph.
 Why? Because human language is imprecise and many words have more than one meaning, and so putting things in proper context helps comprehension. This is why Google’s Multitask Unified Model (MUM), and its AI Overviews (previously known as the Search Generative Experience) are now generating and displaying search results based on relationships, and not just words.
Why? Because human language is imprecise and many words have more than one meaning, and so putting things in proper context helps comprehension. This is why Google’s Multitask Unified Model (MUM), and its AI Overviews (previously known as the Search Generative Experience) are now generating and displaying search results based on relationships, and not just words.
AI-driven data discovery has changed what visibility means.
Sam Altman told Tech Crunch that ChatGPT now has over 800 million active users weekly and handles more than 2.5 billion prompts every single day, and yet fewer than 25% of the most-mentioned brands are also the most-sourced. Search visibility now extends beyond rankings: Brands must be understood as authoritative entities in order to appear in AI summaries, SERPs, and other discovery surfaces.
What does it mean to practise Entity SEO?
Practising Entity SEO involves building your web page’s online presence around the most identifiable concepts or entities present in your copy, rather than just keywords. The goal is to help search engines understand the full context, relationships, expertise, authority, and trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) of your business content. Keyword relevance still matters, but entity clarity now determines whether your content is recognized as the most valuable, authoritative and correct answer in AI Overviews and semantic search.
KPDI takes a four-step approach to Entity SEO
The process begins with a free evaluation which rewards anyone who enquires about the possibilities, with a free report grading their website and showing which opportunities exist with regards to Entity SEO adoption.
-
- 1) Audit and Triage Legacy URLs,
- 2) Rewrite Web Copy for E‑E‑A‑T signals
- 3) Optimize Entity Recognition & Relationships
- 4) Add Corroboration and Monitor
Before Starting, We’ll Research your Entity Map and Compare Competitors’ Entities
- It’s very important to understand the entity you seek to improve, and which type of search you hope to attract, and which types of queries you could most effectively ‘solve’ within your core expertise. This is where the SEO team at KPDI really shines: We can see how search engines will perceive your website’s homepage, and other pages, and the solutions available, in accordance with what they expect to find at your URLs.

-
1) Step One: Audit and Triage Legacy URLs
We start by listing all existing URLs, categorizing them by performance, freshness, and strategic fit metrics such as traffic, impressions, conversions, date of last update, and topical relevance. It’s very important that your content relates to your company’s current positioning, or what we’ve always called its raison d’être. With this in mind, we classify each URL into at least four different categories which are, ‘keep and improve’, ‘consolidate’, ‘noindex / internal only’, or ‘remove / redirect’. Anything else, a fifth column is pruned away and that includes content which is off-topic, duplicate, or too shallow and unimportant to salvage.
The final stage of the triage process is to prioritize which pages to rewrite or edit to amplify the most valuable signals within the Google EEAT framework.
-
2) Rewrite Web Copy for E‑E‑A‑T signals
- The URLs we’ve previously relegated to the Keep & Improve category in our triage process are now reappraised in a priority list, which is, as noted above, the last stage of the triage process.
- Entity Mapping – we use Screaming Frog + AI tools to make models of all the concepts present on a website and all related subjects which add to your topical relevance. The ideas and concepts (entities) within the body of content are quantified to make a Topical Authority score. We also use AI to check our competitors’ pages and determine their Topical Authority scores and strengths. If they’re superior, we will to some extent, emulate their approach and try to surpass them, filling-in the gaps.
- Enhance Experience and Expertise by rewriting content in your experts voice, and by adding first‑hand details. Each blog entry and even some pages should have clear author bylines with credentials. These people should be verifiable subject matter experts where appropriate, but especially for health & finance business websites (YMYL). Clicking my name above, as the author of this article, will access my own biography with links to my LinkedIn profile and other social media websites.
- Strengthen Authoritativeness and Trust by updating facts, citing Primary Sources, and by tightening the focus of each page to match search intent, making sure the content is accurate, well‑organized, and presented inside proper header hierarchies. Additionally, we like to quote experts and link to their bios on professional websites. We practice primary journalism, getting as close as possible to the primary sources of information on subject.
-
3) Optimize Entity Recognition & Relationships
The next step is to tweak each page so its main entity (topic, product, service, or brand) is singularly present in the H1 header, the introductory paragraph, and in the subheadings. We ensure closely related entities are covered in a coherent topic cluster with internal links between pillar and supporting pages.
- Structured data is addressed, and improved. In some instances we may deploy schema automation tools like Schema App (or Merkle), or we add Schema manually to the page headers depending on the situation. The end result is to create consistent entity markup across the client site. By doing Entity Mapping first, we can implement schema which reinforces our audit findings rather than adding markup randomly. We focus on our strongest entity clusters first, and then we expand to supporting topics.
Internal and external links – we label entities in anchor text, with consistent naming, so search engines can recognize the page and understand how it fits into a broader knowledge graph.
Sitemap – Having a flawless sitemap is important in Entity SEO and we use Google Search Console to regularly check page indexing to make sure all topically important pages on the sitemap are indexed. If they’re not being indexed, we check the website navigation to see if it’s even possible for humans to get there through site links, and it it’s not possible, then that must be fixed by adding proper onsite indexes.

What it Means to Optimize for Entities?
We recognize entities as being the atomic units of meaning in Google’s content ecosystem. Important people, products, and concepts, all of which are ‘named things’ form the backbone of the world’s Knowledge Graph. Every piece of content you publish either reinforces or confuses how search engines perceive the existing units. Where traditional SEO focuses on matching words to queries, entity-first optimization is really more about clarifying meanings, by placing things in context, so Google and AI systems can more easily and accurately place your page within their existing semantic networks.
In practice, cognizing entities means optimizing around three pillars:
Every page is its own thing: Every web page we create is about one canonical entity only, and not a range of things where some are more important than others. The way we structure your website affects how it’s perceived and how your concepts’ are weighed and measured. Best practices include aligning your title, H1, and then using the mainEntityOfPage schema to cement each pages’ singular meaning. Then we fit the pages into a structure which best aligns with how AI already perceives the subject.
Comprehensive yet select coverage: Your entire site should collectively (and yet selectively) represent the ideas which are the entities that define your niche because you are essentially assembling your own Knowledge Graph in which each node (page) reinforces your overall topical authority. An auto detailing business will discuss all aspects of their offering but should refrain from listing the makes and models of the cars being displayed in their image gallery as that would engender more connections which are not relevant to their business.
Connect the entities: Entities gain strength through context and so we use internal links and the sameAs reference tag in schema to show relationships (e.g., Product → Category → Brand) tell Google how concepts fit together, improving both discoverability and interpretation. This is also where we might use Wikidata q numbers.
Cement Relationships Between Entities in your Pages
Sometimes the issue is not missing entities, but rather, missing connections between entities. As an example, your website may already have pages being featured in Ai generated answers, and you may even have entities being showcased in Knowledge Panels, but if those topics never reference one another, Google will not see how your pages and real world goods and services relate to one another. We add these connections through contextual links, schema relationships, and or by cross-referencing concepts within your existing content. Ultimately we do all this to help Google understand how your expertise drives their understanding of your offerings.
We Use AI to Discover Emerging Subjects Related to Your Offerings
AI-driven embedding analysis can uncover emerging or adjacent entities before they become mainstream.
Example: A digital marketing agency such as KPDI might structure its ‘app development lifecycle’ page to show how such development initiatives move from planning through to design and then coding, testing, and launching the finished project. The phases would include planning and market research, UX/UI design, development, QA testing, deployment, and post-launch support. Each phase builds on the last to ensure the app is user-focused, technically robust, and continuously improved over time. In other words, all of these concepts and their respective pages are related and their relationship to each other can be demonstrated within the actual structure of our website.
To continue the example, the page has a unique focus and singularly targets mobile application development (Q2988038), consistently using those words in the Page Title, and H1 header, and using the Wikidata Q number in the schema.
Related pages: Other pages with related concepts such as “Coding Apps”, “Testing Apps” and “Launching Apps” would each map to their respective entities, creating distinct nodes under the same semantic hub: mobile application development.
Connecting the concepts: Internal links and sameAs references are used to bind pages together, also connecting the authors and all external sources like Wikidata into a cohesive presentation, reinforcing how each concept fits within your brand’s mini Knowledge Graph.
How Structured Data boosts Entity SEO
Semantic HTML is key to Entity SEO because it works to give search engines clearer meanings and helps structure content around known concepts. Schema tags often define relationships between entities to boost comprehension for AI, leading to better indexing, context, rich snippets, and higher relevance to user queries. Tags like <h1>, <article>, <nav>, and <figure> tell bots what is truly important, and not just how it should appear on the page.
We use Semantic HTML to define concepts and impose structure to make a hierarchy of ideas. We use <h1>, <h2>, <article>, <section> tags to clearly mark main topics, subheadings, and self-contained content, helping search engines grasp the logical flow and importance of information.
Clarifies Entity Relationships: By wrapping content in meaningful tags (e.g., <time> for dates, <figure> for images with captions, <address> for contact info), we provide context that helps bots understand entities (people, places, concepts) and their connections.

KPDI Uses Structured Data for More Precise Entity Identification
For Entity SEO, the most common schemas are Organization, LocalBusiness, and Person for authors and experts to define your core business / identity.
Subject matter experts and their area of expertise can be identified in their published biographies by utilizing the knowsAbout tag.
We use specific Schema types like Product, Article, and FAQ Page for content, all implemented in JSON-LD, to link your brand to authoritative entities and appear in rich snippets for better understanding and visibility.

-
4) Add Corroboration and Monitor
Reinforce E‑E‑A‑T and Entity signals by streamlining citations, directory listings, profiles, and brand mentions. Keep NAP and key descriptors consistent everywhere your entity appears. Monitor rankings, engagement, and conversions for updated URLs and iterate, using scheduled recrawls of your inventory to refresh critical pages regularly so they stay accurate, up‑to‑date, and competitive.
Entity-first optimization unifies technical SEO, content strategy, and data modeling into one shared framework. Schema markup becomes your language for machine interpretation; editorial decisions become signals that reinforce those schema relationships. Together, they create a feedback loop of semantic clarity: What your content says, what your schema encodes, and what search engines understand finally all align.
How does KPDI Measure your AI Visibility Score?
Every SEO client at KPDI is audited and given an AI Visibility Score which estimates how often and even how favorably their branded content appears in AI-generated answers. This applies across platforms like ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity and Google’s AI Overviews. We measure AI Visibility Scores by using third-party tools, primarily Semrush’s AI Search Visibility Checker.
KPDI uses AI Visibility Tools to Measure your Exposure and Potential
Several marketing intelligence platforms offer tools to automate the measurement process. These tools scan AI models for brand mentions and provide a score.
Semrush’s AI Search Visibility Checker: Enter a domain to get an AI visibility score, mention counts, and competitor comparisons across platforms like ChatGPT and Gemini. Sadly, at this time, it doesn’t do Perplexity which is the AI platform of choice in the KPDI SEO dept.
Traditional keyword reporting has always had gaps, and often misrepresents buyers’ intent. AI systems do a better job of interpreting meaning and serving queries with more applicable solutions. Here at KPDI, we are adopting and experimenting with systems which track our clients as entities. We seek to measure how often they appear in AI Overviews, featured snippets, or People Also Ask, and how consistently a brand is cited in knowledge-based answers. We use all the regular tools like Semrush Position Tracking to supplement the AI Visibility Score as described above, by grouping queries under each target entity for a more hybrid view.
SEO Team at KPDI will Design & Deploy your Entity SEO
Entity SEO, the transition from string to things is the next logical step in the evolution of organic Search because it’s more holistic and effective by design.
Semrush’s AI Search and SEO Traffic Study is being quoted in articles similar to this because of their claim and proof that visitors from AI-powered search results convert four times more often than those entering from Google’s organic search. While remarkable, it’s understandable and indicates that AI-enabled consumers generally feel more confident and informed and are thus more capable of making purchase decisions. The piece connects AI visibility to real world business outcomes.
The SEO department at KPDI would be delighted to show you how your content aligns with Google’s entity-understanding knowledge-pipeline, from schema optimization and NLP alignment to entity mapping and cross-team workflows, every page you publish should reinforce who you are, what you offer, and how those ideas connect.
“There are no extra pieces in the universe. Everyone is here because he or she has a place to fill, and every piece must fit itself into the big jigsaw puzzle.” Deepak Chopra